When Did Diamond Mining Start in Africa?
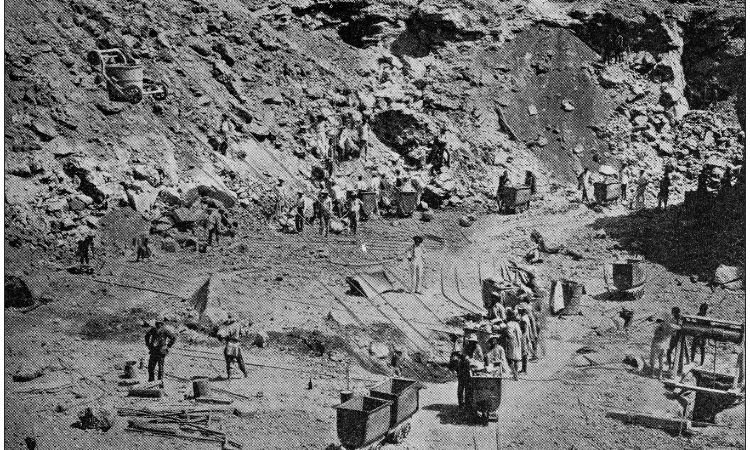

Diamond mining in Africa began in the late 19th century, with the discovery of diamonds in South Africa marking the start of large-scale commercial diamond extraction on the continent.
Here’s a concise overview of the history and development of diamond mining in Africa.
1. Early Diamond Discoveries in Africa
The first recorded discovery of diamonds in Africa occurred in South Africa in 1866, when a 15-year-old boy named Erasmus Jacobs found a transparent rock on his father’s farm near the Orange River. This was the first diamond found in Africa, and it launched the continent into the global diamond industry.

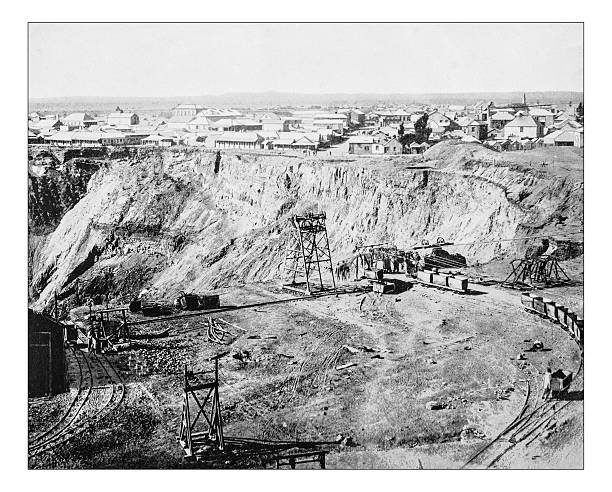
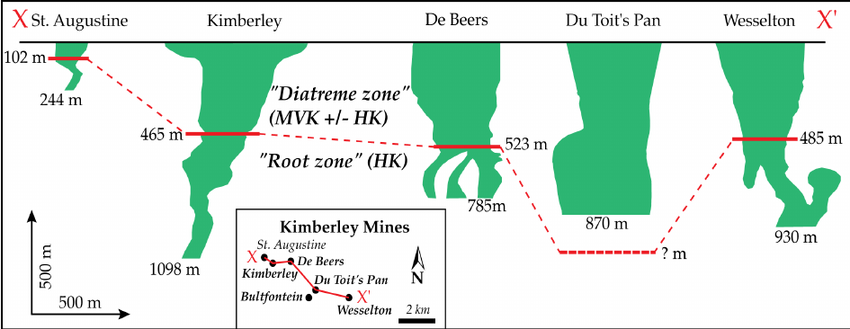
2. The Kimberley Diamond Rush (1870s)
In 1871, the discovery of diamonds near Kimberley, South Africa, led to a massive diamond rush. The Kimberley Mine (also known as the Big Hole) became one of the most famous diamond mines in the world.
- Key event: The discovery of diamonds in alluvial deposits and kimberlite pipes
- Impact: Formation of De Beers Mining Company by Cecil Rhodes in 1888
- Result: South Africa became the world’s leading diamond producer by the end of the 19th century

3. Expansion Across Africa
Following South Africa’s success, diamond mining expanded to other African countries in the 20th century, especially after World War II:
- Angola: Commercial diamond mining began in the 1920s, with large-scale production increasing in the post-independence era.
- Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): Diamonds were discovered in the 1920s, and DRC became a major producer.
- Sierra Leone: Mining expanded in the 1930s, and the country became known for high-quality alluvial diamonds.
- Tanzania and Lesotho: Later entrants, with significant production beginning in the 1950s–1960s.
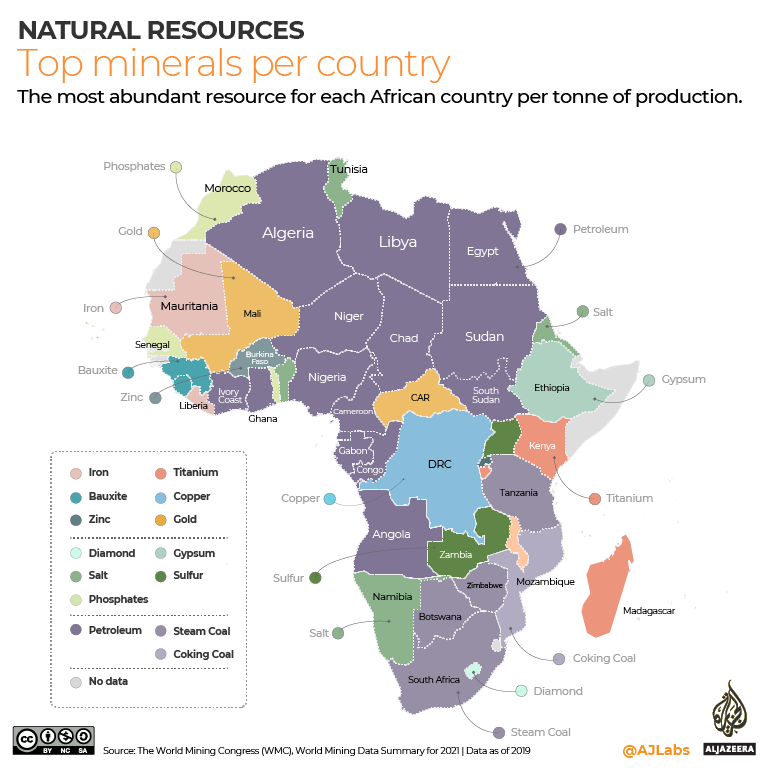
4. Types of Diamond Deposits in Africa
African diamonds are found in two main geological settings:
- Kimberlite pipes: Volcanic formations that host diamonds deep in the Earth’s crust (e.g., South Africa, Lesotho)
- Alluvial deposits: Diamonds eroded from primary sources and deposited in rivers and coastal areas (e.g., Angola, Sierra Leone)
These deposits vary in accessibility and mining methods used.
5. Diamond Mining Today in Africa
Africa remains a major global source of diamonds, with Botswana, Angola, South Africa, and Namibia leading in industrial diamond production, while artisanal mining is common in DRC and Sierra Leone.
- Botswana: Now Africa’s largest diamond producer by value
- Namibia: Known for high-value marine diamond mining off the coast
- Conflict Diamonds: Some regions were associated with “blood diamonds” during civil wars in the 1990s, leading to the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme

FAQs
Q1: When did diamond mining start in Africa?
A1: It began in 1866 in South Africa, with the discovery of the first diamond by Erasmus Jacobs.
Q2: Which African country started diamond mining first?
A2: South Africa was the first African country to begin commercial diamond mining.
Q3: What is the Kimberley Process?
A3: An international certification scheme established in 2003 to prevent the trade in conflict diamonds.
Conclusion
Diamond mining in Africa started in 1866 in South Africa, and has since expanded across the continent. Today, Africa remains a major global supplier of diamonds, playing a vital role in the economies of several nations and the global jewelry and industrial diamond markets.

