What are the conflict minerals in Congo
What Are the Conflict Minerals in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC)?
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is rich in natural resources, but some of its minerals have been linked to armed conflict and human rights abuses. These minerals are commonly referred to as “conflict minerals” due to their role in funding violence and instability in the region.
Here are the four main conflict minerals associated with the DRC:
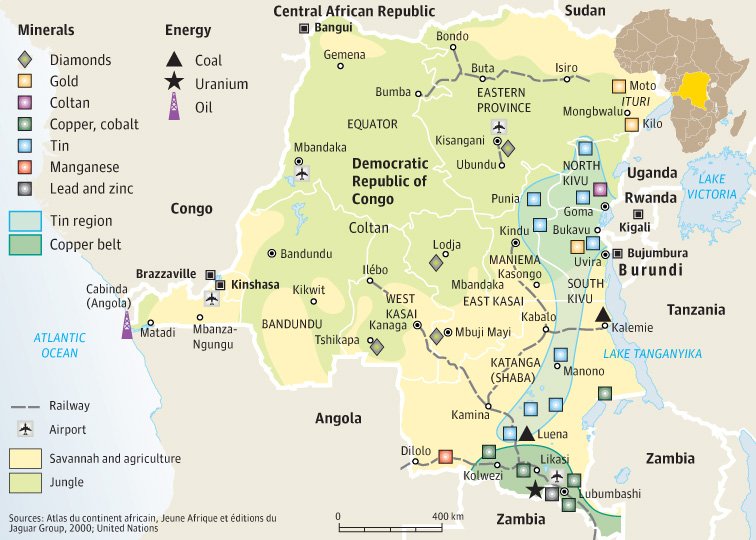
1. Tin (Cassiterite)
Tin is used in soldering materials for electronics and construction. In the DRC, cassiterite (the ore from which tin is extracted) is often mined in areas controlled by armed groups , with profits fueling local conflicts.
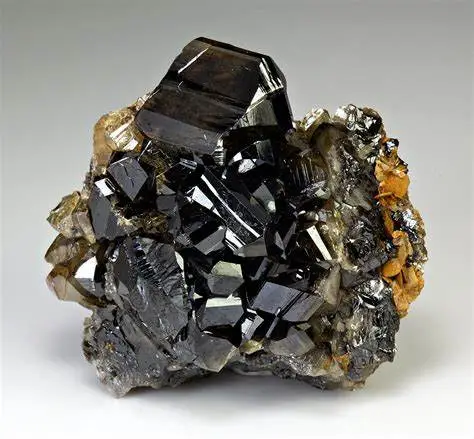

2. Tungsten (Wolframite)
Tungsten is valued for its high melting point and is used in lightbulbs, drills, and weapons . Wolframite, the main source of tungsten, is frequently mined in eastern DRC under poor labor conditions and used to fund armed militias.

3. Tantalum (Coltan)
Tantalum, derived from coltan (columbite-tantalite) , is essential for capacitors in smartphones, laptops, and gaming devices . The demand for coltan has driven illegal mining and exploitation in conflict-affected regions of the DRC.

4. Gold (Au)
Gold from the DRC often comes from artisanal mines controlled by armed groups. The illicit gold trade funds violence and corruption, undermining peace and economic development in the region.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What defines a conflict mineral?
A: A conflict mineral is any mineral mined in conditions of armed conflict and human rights abuses, often funding warlords or rebel groups.
Q: Are all minerals from the DRC considered conflict minerals?
A: No, not all minerals from the DRC are conflict minerals. Many are sourced responsibly, but minerals from eastern DRC , especially tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold , are most commonly associated with conflict.
Q: How are companies addressing conflict minerals?
A: Many global companies follow U.S. regulations (Dodd-Frank Act) and OECD guidelines to ensure their supply chains are free from conflict minerals. This includes due diligence and traceability measures.

