Mining Law in Africa
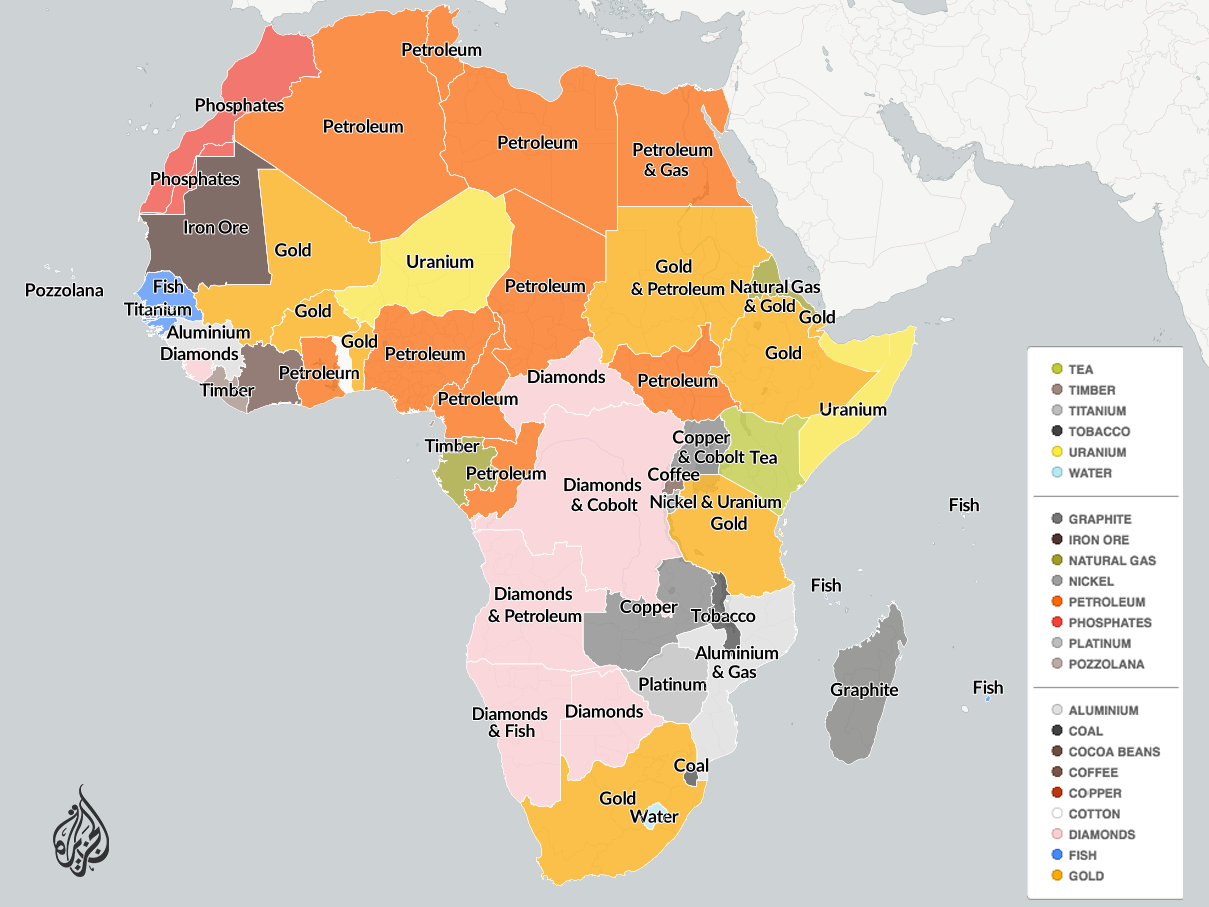
The mining industry in Africa is governed by a complex web of national laws , international treaties , and regulatory bodies that aim to ensure responsible resource extraction, protect local communities, and promote sustainable development. As one of the most resource-rich continents, Africa’s mining sector is under increasing scrutiny for its environmental impact, labor practices, and economic benefits.
Overview of Mining Law in Africa
Mining laws vary from country to country, but they generally cover:
- Licensing and Permitting : Rules for obtaining exploration and mining rights.
- Environmental Protection : Regulations on waste management, land restoration, and pollution control.
- Community Engagement : Requirements for consulting with local populations and ensuring fair compensation.
- Taxation and Revenue Sharing : Laws governing how mineral revenues are collected and distributed.
- Corporate Responsibility : Standards for labor rights, health and safety, and corporate accountability.
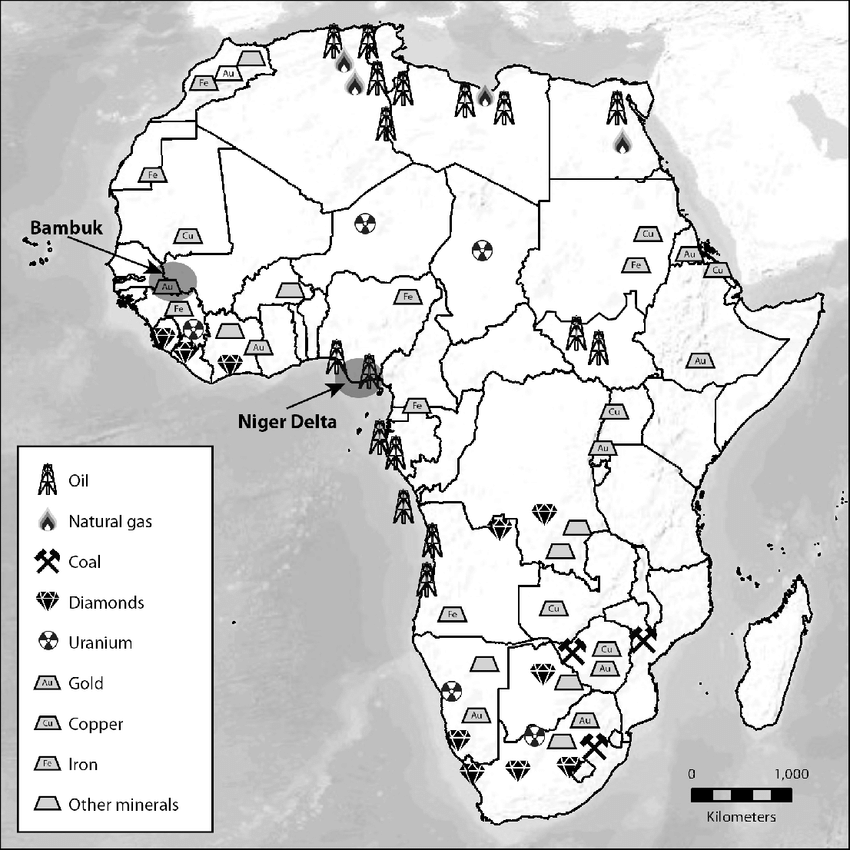
Key Elements of Mining Law in Africa
1. National Mining Legislation
Each African country has its own mining code or law , which outlines the legal framework for mineral exploration and extraction. For example:
- South Africa : Governed by the Mineral Resources and Petroleum Development Act (2004) , which emphasizes transformation, local content, and community participation.
- Zambia : Regulated by the Mining Act (2015) , which focuses on transparency, revenue sharing, and environmental protection.
- Ghana : Overseen by the Minerals and Mining Act (2019) , which promotes sustainable mining and local ownership.
2. International Agreements and Treaties
Several international agreements influence mining law in Africa, including:
- The Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI) : Encourages transparency in the oil, gas, and mining sectors.
- The Kimberley Process : Regulates the trade of rough diamonds to prevent conflict diamonds.
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) : Applies to certain minerals and wildlife products.
3. Environmental Regulations
With growing concerns about climate change and ecological damage, many African countries have strengthened their environmental regulations for mining activities. These include:
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs)
- Rehabilitation and Reclamation Requirements
- Water and Air Quality Standards

4. Land Rights and Community Consultation
In many African countries, land rights and community consultation are central to mining law. This includes:
- Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) for indigenous and local communities.
- Compensation for land use and displacement .
- Participation in decision-making processes related to mining projects.
Challenges in Mining Law Enforcement
Despite the existence of legal frameworks, several challenges persist in enforcing mining laws across Africa:
- Corruption and Weak Governance : Some governments lack the capacity or political will to enforce regulations effectively.
- Lack of Transparency : Illicit mining and informal operations often operate outside the legal system.
- Disputes Over Land and Resources : Conflicts between mining companies, local communities, and governments can lead to legal disputes.
- Limited Access to Justice : Many affected communities face barriers in accessing legal remedies or participating in regulatory processes.

The Role of International Organizations
Organizations like the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) , World Bank , and African Union play a key role in supporting legal reforms , capacity building , and policy development in the mining sector.
FAQs
Q: What is mining law in Africa?
A: Mining law in Africa refers to the set of national and international regulations that govern the exploration, extraction, and management of mineral resources.
Q: Do all African countries have mining laws?
A: Yes, every African country has some form of mining legislation, though the scope and enforcement vary.
Q: How do international agreements affect mining law in Africa?
A: International agreements like EITI and the Kimberley Process help promote transparency, accountability, and ethical mining practices.
Q: Are there environmental regulations for mining in Africa?
A: Yes, many African countries have environmental laws that require mining companies to conduct impact assessments and follow sustainability guidelines.
Q: Can local communities influence mining laws in Africa?
A: Yes, through public consultations, legal challenges, and advocacy efforts, local communities can play a role in shaping mining policies.

