Mining in Africa – Key Notes (2025)
1. Overview
- Mining is a core economic sector across Africa.
- The continent holds vast reserves of precious metals, base metals, gemstones, industrial minerals, and critical raw materials .
- Africa contributes significantly to global supply chains, especially for green energy and digital technologies .
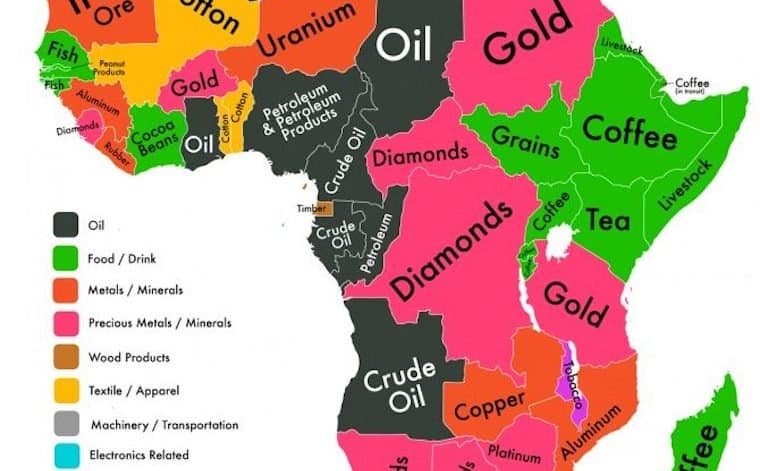
2. Major Minerals & Top Producing Countries
| Gold | Ghana, South Africa, Mali, Burkina Faso | Jewelry, electronics, reserves |
| Diamonds | Botswana, DRC, Angola, Namibia | Gemstones, cutting tools |
| Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) | South Africa (80%+ world supply) | Catalytic converters, hydrogen tech |
| Cobalt | Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) (~70% global output) | EV batteries, aerospace |
| Copper | DRC, Zambia | Electrical wiring, renewables |
| Lithium | Zimbabwe, Namibia, Mali | Battery storage, electric vehicles |
| Bauxite | Guinea (largest reserves globally), Ghana | Aluminum production |
| Phosphate Rock | Morocco (70% of world reserves), Tunisia | Fertilizers |
| Iron Ore | South Africa, Mauritania, Liberia | Steel manufacturing |
| Uranium | Niger, Namibia, South Africa | Nuclear energy |
3. Geological Wealth: Why Is Africa So Rich in Minerals?
- Ancient Precambrian cratons (stable continental cores) formed over 2 billion years ago.
- Tectonic activity created mineral-rich formations like:
- Witwatersrand Basin (SA) – Gold
- Central African Copperbelt (DRC/Zambia) – Copper & cobalt
- Kimberlite Pipes – Diamonds
- Favorable conditions for deposits of diamonds, gold, PGMs, and lithium-bearing pegmatites.
4. Economic Importance
✅ Positive Impacts:
- Contributes 5–35% of GDP in major mining nations (e.g., Botswana, DRC, Guinea).
- Generates government revenue through taxes, royalties, and state equity .
- Creates over 1 million direct jobs and supports millions more indirectly.
- Attracts foreign direct investment (FDI) from China, Canada, Australia, and Europe.
- Funds infrastructure development (roads, rail, power near mine sites).
⚠️ Challenges (Resource Curse):
- Over-reliance on commodity prices → economic volatility
- Revenue mismanagement and corruption
- Limited local processing (“exporting rocks”)
- Environmental degradation
- Social conflicts and displacement
5. Types of Mining
| Large-Scale Industrial Mining | Mechanized operations by multinational companies | Anglo American, Barrick Gold, Eurasian Resources Group |
| Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM) | Manual extraction by individuals or small groups | ~40 million people depend on ASM in Africa |
| Open-Pit Mining | Surface excavation for shallow deposits | Copper mines in Zambia |
| Underground Mining | Deep tunnels for deep ore bodies | Gold mines in South Africa |
| Alluvial Mining | Extracting minerals from riverbeds/sediments | Diamond panning in Sierra Leone |
6. Social & Environmental Issues
- Child labor and unsafe working conditions in informal mining (especially cobalt in DRC)
- Deforestation, water pollution, acid mine drainage
- Land degradation and loss of farmland
- Displacement of communities without fair compensation
- Air and noise pollution near processing plants
🟢 Improving Practices:
- Adoption of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) standards
- Land reclamation and biodiversity programs
- Community development agreements
- Use of renewable energy in mining operations
7. Ethical & Regulatory Frameworks
- Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS): Prevents trade in conflict diamonds (since 2003)
- OECD Due Diligence Guidance: For responsible mineral supply chains
- Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI): Promotes openness in revenue reporting
- National agencies regulate licensing, safety, and environmental compliance
8. China’s Role in African Mining
- Major investor and buyer of African minerals
- Funds infrastructure in exchange for resource access (“infrastructure-for-resources” deals)
- Operates numerous mines and processing facilities
- Criticized for lack of transparency and environmental concerns — but also praised for job creation
Examples: Zijin Mining, CMOC (Tenke Fungurume, DRC), Sinomach, Huaxia Mining
9. Future of Mining in Africa
🔮 Trends shaping the future:
- Rising demand for critical minerals (lithium, cobalt, graphite) for EVs and clean energy
- Push for mineral beneficiation — processing ores locally instead of exporting raw materials
- Investment in green mining : solar-powered operations, water recycling
- Digitalization: use of drones, AI, and blockchain for traceability
- Youth employment initiatives and skills training in mining regions
🎯 Goal: Transform Africa from a raw material exporter into a value-added processor and global green economy partner .
✅ Summary: Key Takeaways
- Africa is geologically rich and strategically vital to the global economy.
- Mining drives growth but requires better governance and sustainability .
- Ethical sourcing, community inclusion, and local processing are essential for long-term success.
- The continent has a historic opportunity to leverage its mineral wealth for inclusive development .

