Mining in Africa
Africa is one of the most resource-rich continents on the planet, with an extensive range of minerals that have shaped its economy for centuries. From gold and diamonds to rare earth elements and precious metals, the African mining industry plays a vital role in both local development and global markets. As demand for critical minerals continues to rise—especially for renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles—the importance of Africa’s mining sector is growing exponentially.
Key Mining Regions in Africa
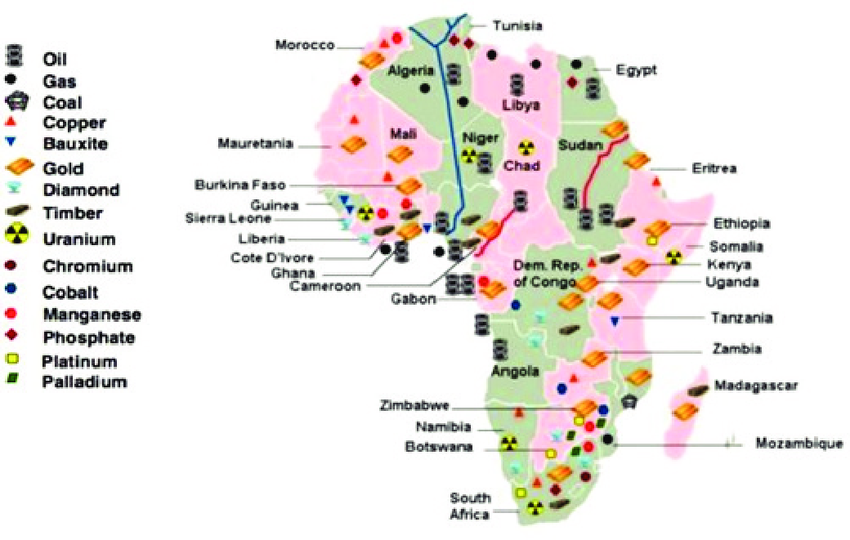
A detailed map of Africa highlights the major areas where mining activities are concentrated. These regions are rich in various types of minerals, including:
- Gold : South Africa, Ghana, Mali, Burkina Faso
- Diamonds : Botswana, Angola, Sierra Leone, Namibia
- Copper & Cobalt : Zambia, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Tanzania
- Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) : South Africa, Zimbabwe
- Oil & Gas : Nigeria, Algeria, Sudan, Libya
- Coal & Iron Ore : Mozambique, South Africa, Nigeria
This geographic distribution shows how mining is not limited to one region but spans across the continent, supporting millions of jobs and driving economic growth in many African nations.
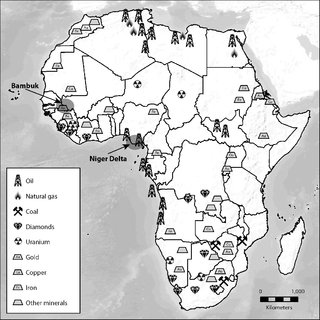
Economic Impact of Mining in Africa
Mining has long been a cornerstone of economic development in many African countries. It contributes significantly to GDP, provides employment opportunities, and generates foreign exchange through exports. For instance, South Africa’s mining sector has historically driven industrialization, while the DRC’s cobalt and copper mines are increasingly important for global technology supply chains.
As the world transitions toward green energy, the demand for minerals like lithium, nickel, and manganese is rising. This presents new opportunities for African countries to expand their mining industries and attract foreign investment.

Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its potential, the African mining industry faces several challenges. Environmental concerns, such as deforestation, water pollution, and land degradation, are significant issues. Additionally, political instability, corruption, and lack of infrastructure can hinder sustainable development.
However, with increased investment, better governance, and stronger community engagement, the future of mining in Africa looks promising. Countries are beginning to focus more on responsible mining practices, ensuring that local communities benefit from mineral wealth and that environmental impacts are minimized.
FAQs
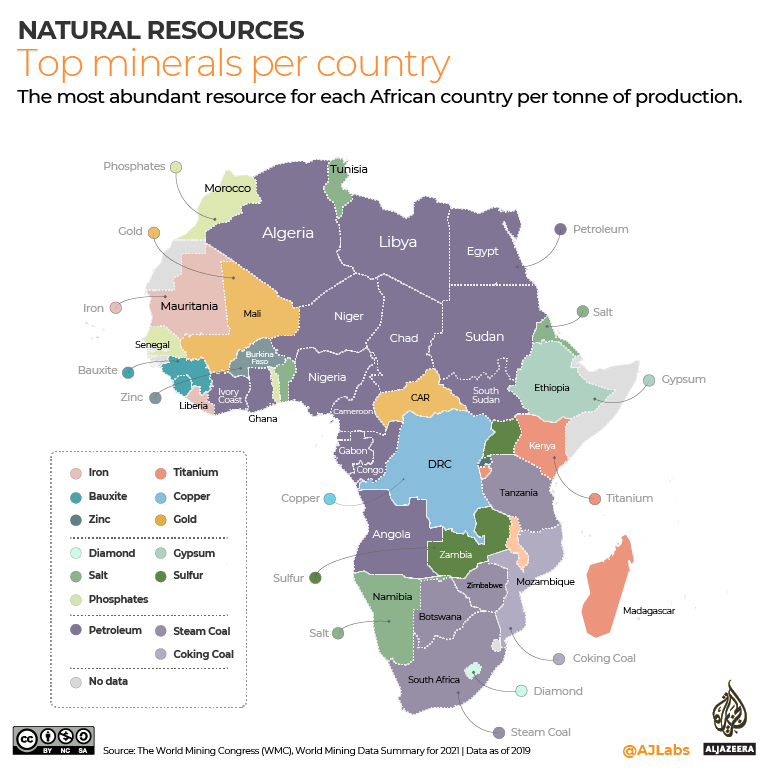
Q: Which African country is the largest producer of gold?
A: South Africa has historically been the largest producer of gold in Africa, though other countries like Ghana and Mali are also major contributors.
Q: Are there oil reserves in Africa?
A: Yes, several African countries, including Nigeria, Algeria, and Sudan, have substantial oil reserves and are major players in the global oil market.
Q: How does mining affect the environment in Africa?
A: Mining can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, water contamination, and loss of biodiversity. However, many companies and governments are now adopting more sustainable practices to reduce these negative effects.
Q: What role does Africa play in the global supply of rare earth elements?
A: While not as dominant as China, Africa is emerging as a key player in the production of rare earth elements, which are essential for electronics and clean energy technologies. Countries like Malawi and South Africa are investing in this area.

