Industrial Minerals and Geology

Industrial minerals are essential to modern life, used in everything from construction materials to cosmetics. But how do these minerals form, and why are they found in specific regions?
Understanding the geology of industrial minerals helps us locate, extract, and utilize them responsibly—ensuring both economic value and environmental sustainability.
What Are Industrial Minerals?
Industrial minerals are naturally occurring, non-metallic minerals used in industrial applications. Unlike metals or fuels, they are valued for their physical and chemical properties , not for energy or metallic content.
Common industrial minerals include:
- Limestone (calcium carbonate)
- Kaolin (china clay)
- Silica Sand (quartz)
- Talc
- Gypsum
- Bentonite
- Feldspar
Each mineral has a unique geological origin and set of characteristics that determine its industrial use.
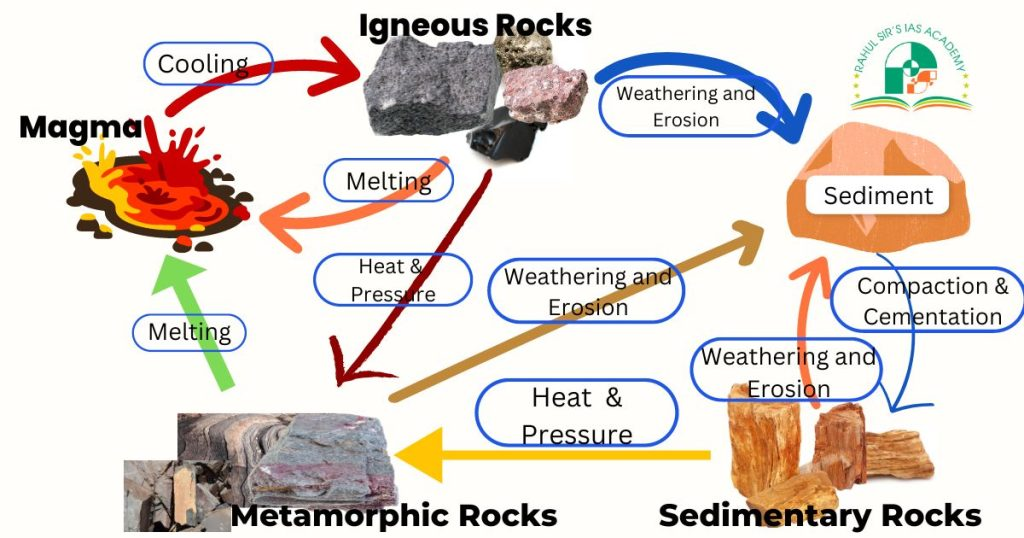
How Do Industrial Minerals Form?
Industrial minerals form through a variety of geological processes , including:
1. Sedimentary Processes
Minerals like limestone , gypsum , and halite (rock salt) form from the deposition and crystallization of minerals in water bodies such as oceans, lakes, and evaporating basins.
2. Weathering and Alteration
Kaolin and bauxite often form through the chemical weathering of rocks like granite or basalt under tropical or humid conditions.
3. Metamorphic and Hydrothermal Activity
Talc and graphite can form through metamorphism , where existing rocks are altered by heat and pressure. Some clays and silica deposits form from hydrothermal fluids .
4. Volcanic and Igneous Activity
Feldspar and silica sand are often derived from the weathering of igneous rocks like granite and basalt.
Understanding these processes helps geologists identify potential mineral deposits and assess their economic viability .
Why Geology Matters in Industrial Mineral Exploration
- Deposit Location : Geology determines where minerals are likely to be found.
- Purity and Quality : The geological environment affects the purity, grain size, and chemical composition of a mineral.
- Extraction Methods : Knowing the rock type and structure helps in planning mining and processing techniques .
- Sustainability : Understanding geology supports responsible mining , land reclamation, and resource longevity .
As industries move toward greener practices, the geological understanding of industrial minerals becomes even more crucial in reducing environmental impact and improving efficiency.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the geological origin of kaolin?
A: Kaolin typically forms from the chemical weathering of feldspar-rich rocks like granite under warm, humid conditions.
Q2: Where are silica sand deposits commonly found?
A: Silica sand is often found in ancient riverbeds, beaches, and sandstone formations , formed by the erosion and weathering of quartz-rich rocks.
Q3: How does geology affect the use of industrial minerals?
A: The geological formation influences the purity, structure, and properties of a mineral, which in turn determines its industrial suitability and application .

