Emerald Mining in Africa
Emerald Mining in Africa: Unveiling the Continent’s Green Treasures
Emeralds, one of the most coveted gemstones in the world, are prized for their vibrant green hue and rarity. Africa is home to some of the finest emerald deposits on the planet, with countries like Zambia, Ethiopia, and Zimbabwe leading the way in production. The continent’s emerald mining industry not only supplies the global gemstone market but also supports local economies through job creation and export revenues. In this blog post, we will explore the fascinating world of emerald mining in Africa, supported by vivid image descriptions and insights into its opportunities and challenges.

Zambia: The Emerald Powerhouse
Zambia is the world’s second-largest producer of emeralds, accounting for approximately 20% of global output. The Kagem mine, operated by Gemfields, is the largest emerald mine in the world. Zambian emeralds are renowned for their rich color and clarity, making them highly sought after in international markets. The industry provides thousands of jobs and contributes significantly to the country’s economy.
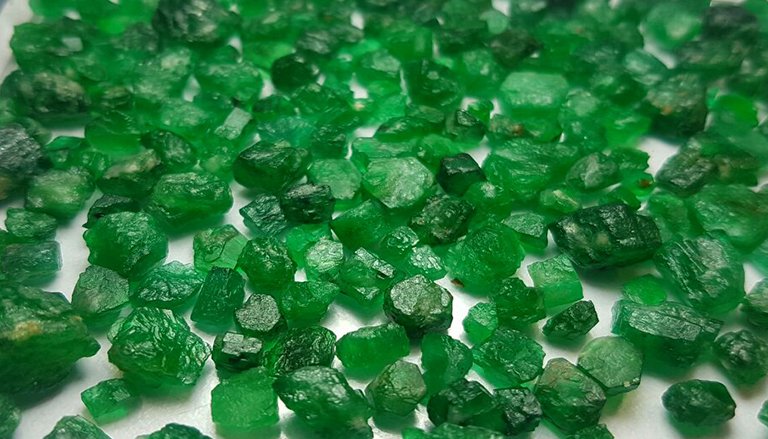

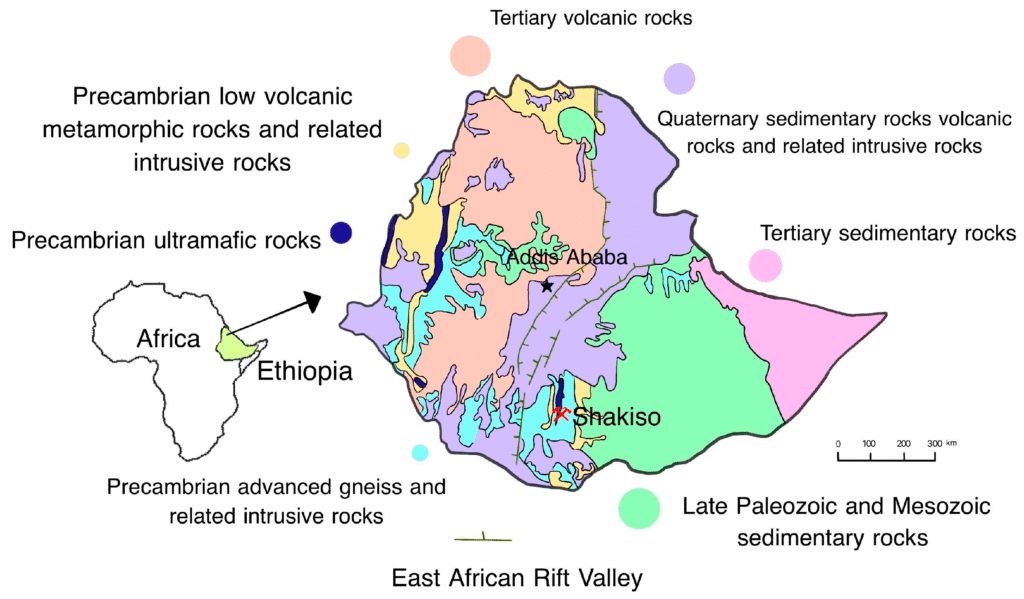
Ethiopia: The Rising Star
Ethiopia has emerged as a new player in the global emerald market, thanks to discoveries in the Seba Boru region. Ethiopian emeralds are noted for their unique bluish-green hue and exceptional quality. While still in its early stages, the country’s emerald mining sector holds immense promise for economic growth and development.
Zimbabwe: Hidden Gems
Zimbabwe’s Sandawana Valley is known for producing high-quality emeralds, often smaller in size but prized for their intense green color. Artisanal miners dominate the sector, though efforts are underway to formalize operations and attract foreign investment. Zimbabwean emeralds are gaining recognition in niche markets for their unique characteristics.

Environmental and Social Impacts
Environmental Concerns
Emerald mining can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution, particularly in regions with inadequate regulations. Rehabilitating mined areas and adopting sustainable practices are essential to minimizing environmental damage.
Community Benefits and Challenges
While emerald mining creates jobs and stimulates local economies, it can also lead to displacement and social conflicts if not managed responsibly. Ensuring fair compensation, providing community development programs, and fostering transparency are key to balancing economic benefits with social well-being.
Opportunities in African Emerald Mining
1. Global Market Demand
The demand for high-quality emeralds continues to grow, driven by jewelry manufacturers and collectors. Africa’s emerald resources are well-positioned to meet this demand, particularly as other traditional sources decline.
2. Value Addition through Cutting and Polishing
Currently, most African emeralds are exported in rough form, limiting revenue potential. Developing local cutting and polishing industries could increase value addition and create additional jobs, reducing reliance on foreign processing centers.
3. Sustainable Practices
Adopting eco-friendly mining techniques, such as reduced water usage and land rehabilitation, can enhance the industry’s sustainability and align it with global standards for responsible sourcing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Which African country produces the most emeralds?
A1: Zambia is the largest emerald producer in Africa, followed by Ethiopia and Zimbabwe.
Q2: Why are Zambian emeralds so valuable?
A2: Zambian emeralds are prized for their deep green color, clarity, and fewer inclusions compared to emeralds from other regions.
Q3: What are the environmental impacts of emerald mining?
A3: Emerald mining can cause deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution. Sustainable practices are needed to mitigate these effects.

