Coal mining in Africa
Coal Mining in Africa: Energy Source, Economic Contributor, and Environmental Challenge
Coal remains a major energy source in several African countries, despite growing global pressure to reduce fossil fuel dependence. While Africa contributes only a small share of global coal production , it plays a significant role in regional economies and energy security , particularly in Southern Africa .
Here are five key aspects of coal mining in Africa :

1. South Africa – The Largest Coal Producer in Africa
South Africa is by far Africa’s largest coal producer and exporter , accounting for over 90% of the continent’s output . The country relies heavily on coal for electricity generation , with Eskom using it to power more than 70% of the national grid .
Key coalfields are located in the Witbank, Highveld, and Waterberg coal basins , supporting both domestic energy needs and export markets in Asia and Europe .

2. Mozambique – Emerging Coal Exporter
Mozambique has become a major coal exporter , particularly from the Moatize coal basin in Tete Province. The mine, operated by Rio Tinto and other firms , produces metallurgical and thermal coal for steelmaking and power generation in Asia and India .
Despite its potential, development has been slowed by infrastructure challenges, political instability , and climate-related disruptions .

3. Zimbabwe – Coal for Power and Industry
Zimbabwe relies on coal for most of its electricity generation , with the Hwange coalfield being the main source. The government is also exploring new coal-fired power projects to address chronic energy shortages.
However, coal mining in Zimbabwe faces challenges such as aging infrastructure, underinvestment , and environmental concerns .

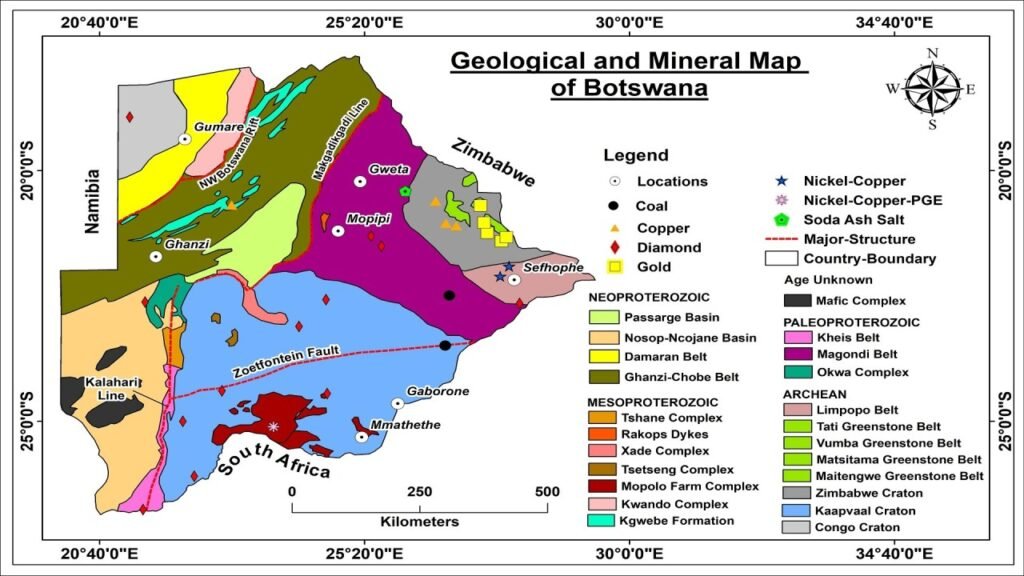
4. Botswana – Developing Coal Resources for Energy Independence
Botswana is investing in coal mining and coal-fired power generation to reduce its dependence on South African electricity imports . Projects like the Morupule Coal Mine and Power Plant aim to boost domestic energy production , though progress has been slow due to technical and financial constraints .
5. Environmental and Economic Impacts
While coal supports energy access and industrial growth , it also raises significant environmental and health concerns , including:
- Air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions
- Water contamination and land degradation
- Health risks for nearby communities
As global pressure increases to shift toward renewable energy , African countries are facing a complex balancing act between economic development and climate responsibility .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Which African country produces the most coal?
A: South Africa is the largest coal producer in Africa , followed by Mozambique and Zimbabwe .
Q: Why is coal important in Africa?
A: Coal is a major source of electricity generation and industrial fuel , particularly in Southern Africa , where it supports energy access and economic growth .
Q: Is Africa expanding coal mining?
A: Some countries like Zimbabwe and Botswana are exploring new coal projects, while others, including South Africa , are under increasing pressure to phase out coal in favor of renewable energy .

