Africa Mining Union: Uniting the Continent’s Mineral Wealth for Sustainable Growth
The Africa Mining Union (AMU) represents a bold vision for collaboration, innovation, and sustainable development across Africa’s mining sector. As the continent holds over 30% of the world’s mineral reserves—including gold, platinum group metals (PGMs), diamonds, cobalt, and rare earth elements—there is immense potential to leverage these resources for economic transformation. However, fragmented policies, regulatory uncertainty, and limited regional cooperation have hindered progress. The concept of an Africa Mining Union seeks to address these challenges by fostering unity, promoting equitable benefit-sharing, and driving investment into the sector. In this blog post, we will explore the idea of the Africa Mining Union, its objectives, potential benefits, and the path toward implementation.

What is the Africa Mining Union?
The Africa Mining Union is a proposed pan-African initiative aimed at harmonizing mining policies, promoting cross-border collaboration, and ensuring sustainable resource management. Inspired by successful regional bodies like the European Union (EU) and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) , the AMU would serve as a platform for governments, private companies, and communities to work together toward shared goals.
The union would focus on:
- Streamlining regulations to attract investment.
- Promoting value addition through local processing and manufacturing.
- Ensuring environmental sustainability and social responsibility.
- Facilitating knowledge-sharing and technology transfer across the continent.
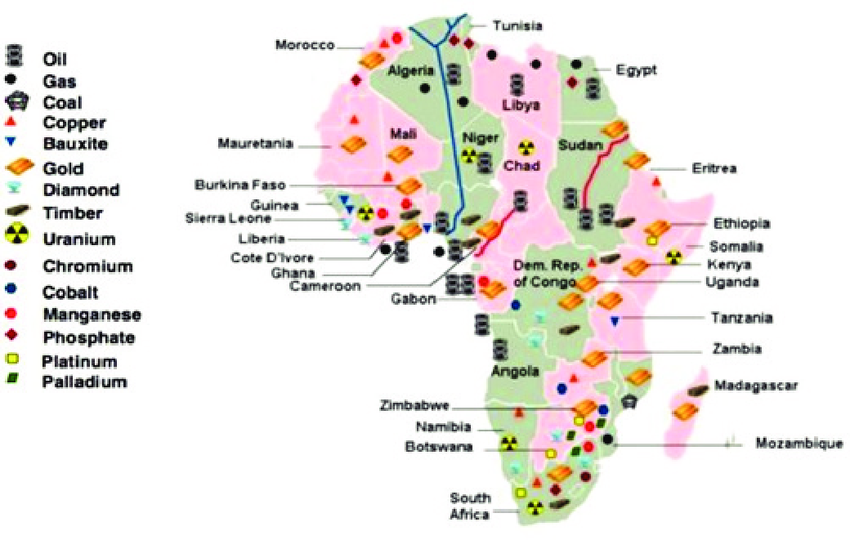
Objectives of the Africa Mining Union
1. Harmonization of Mining Policies
By standardizing mining laws and regulations across member countries, the AMU would reduce regulatory uncertainty and create a more predictable environment for investors. This includes aligning licensing processes, royalty structures, and environmental standards.
2. Regional Collaboration
The union would encourage cross-border mining projects, infrastructure development, and supply chain integration. For example, shared railways and ports could facilitate the transportation of minerals from landlocked countries like Zambia and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).

3. Equitable Benefit-Sharing
The AMU would ensure that mining revenues are distributed fairly among governments, companies, and local communities. This includes funding community development projects, education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
4. Sustainable Practices
Promoting eco-friendly mining practices, such as renewable energy integration, water recycling, and land rehabilitation, would help minimize the environmental impact of mining activities.
5. Capacity Building and Skills Development
The union would invest in training programs to bridge skills gaps, empower local workforces, and prepare them for modern mining roles, including automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and green technologies.
Potential Benefits of the Africa Mining Union
1. Enhanced Investment Opportunities
A unified regulatory framework would attract foreign direct investment (FDI) by reducing risks associated with inconsistent policies. Investors would benefit from streamlined processes and greater transparency.
2. Increased Value Addition
By promoting local processing and manufacturing, the AMU would enable African countries to capture more value from their mineral resources. For example, refining raw cobalt in the DRC or producing lithium-ion batteries in Namibia could boost export revenues.
3. Job Creation and Economic Growth
Unified efforts would lead to the creation of millions of jobs, from skilled roles like engineers to unskilled labor positions. This would drive inclusive economic growth and reduce unemployment rates.
4. Improved Infrastructure
Cross-border mining projects would necessitate the development of shared infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and power plants. These investments would benefit not only the mining sector but also surrounding communities.

5. Strengthened Global Position
By presenting a united front, African nations could negotiate better terms with global buyers and stakeholders, ensuring fair prices for their mineral exports.
Challenges to Implementation
1. Political and Economic Differences
African countries have varying levels of political stability, economic development, and regulatory frameworks. Aligning these differences under a single union would require significant diplomatic effort.
2. Resistance to Change
Some governments and private companies may resist changes to existing policies, fearing loss of control or reduced profitability. Overcoming this resistance will require strong leadership and clear communication of benefits.
3. Funding and Resources
Establishing and maintaining the AMU would require substantial financial and human resources. Securing funding from international organizations, donor agencies, and member states would be essential.
4. Balancing National Interests
While the AMU aims for regional collaboration, individual countries may prioritize their national interests. Striking a balance between collective goals and sovereign priorities is crucial.
Case Studies: Lessons from Regional Initiatives
1. Southern African Development Community (SADC)
The SADC has successfully promoted regional integration in mining through initiatives like shared infrastructure projects and harmonized policies. The AMU could build on these successes by expanding its scope to include all African nations.
2. African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)
The AfCFTA demonstrates the potential of pan-African collaboration to boost trade and economic growth. The AMU could adopt similar principles to enhance intra-African mining partnerships.
3. European Union Raw Materials Alliance (ERMA)
The ERMA focuses on securing critical minerals for Europe’s green transition. The AMU could emulate its model to position Africa as a key supplier of minerals for global clean energy initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the Africa Mining Union?
A1: The Africa Mining Union is a proposed initiative to unify Africa’s mining sector by harmonizing policies, promoting collaboration, and ensuring sustainable resource management.
Q2: How would the AMU benefit African countries?
A2: Benefits include enhanced investment opportunities, increased value addition, job creation, improved infrastructure, and strengthened global bargaining power.
Q3: What are the main challenges to implementing the AMU?
A3: Key challenges include political and economic differences, resistance to change, funding constraints, and balancing national interests with collective goals.
