Africa Mining and Crushing
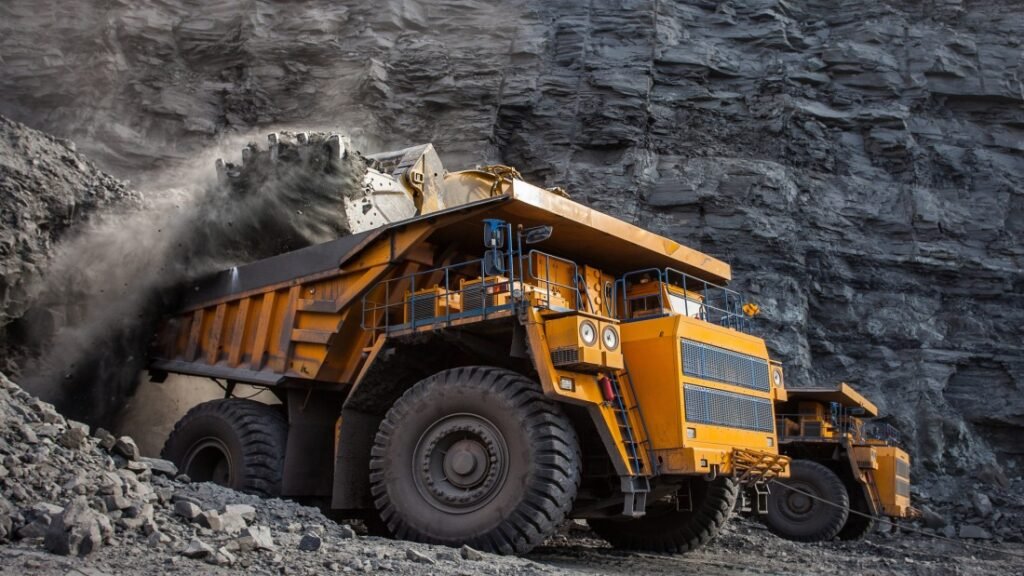

Mining and crushing in Africa are critical stages in the extraction and processing of valuable minerals such as gold, diamonds, copper, cobalt, lithium, and iron ore. Once minerals are mined from the earth, crushing is the first step in breaking down raw ore into smaller particles for further processing and refinement.
Here’s a concise overview of mining and crushing operations across Africa, their importance, methods, and impact.
1. Overview of Mining and Crushing in Africa
Mining in Africa involves extracting minerals from surface or underground deposits, followed by crushing and grinding to liberate valuable ores from waste rock. This process is essential for efficient mineral recovery and downstream processing like flotation, leaching, or smelting.
2. Common Minerals Mined and Crushed
Africa produces a wide range of minerals that undergo crushing during processing:
- Gold: Crushed before cyanide leaching
- Copper and Cobalt (DRC, Zambia): Ore is crushed for flotation and hydrometallurgical recovery
- Diamonds (Botswana, Angola): Crushed carefully to avoid damaging gemstones
- Lithium (Zimbabwe, Namibia): Spodumene-bearing pegmatites are crushed for concentration
- Iron Ore (Liberia, South Africa): Crushed and screened for pelletizing
- Manganese and Bauxite: Also processed through crushing and beneficiation
3. Stages of Crushing in African Mines
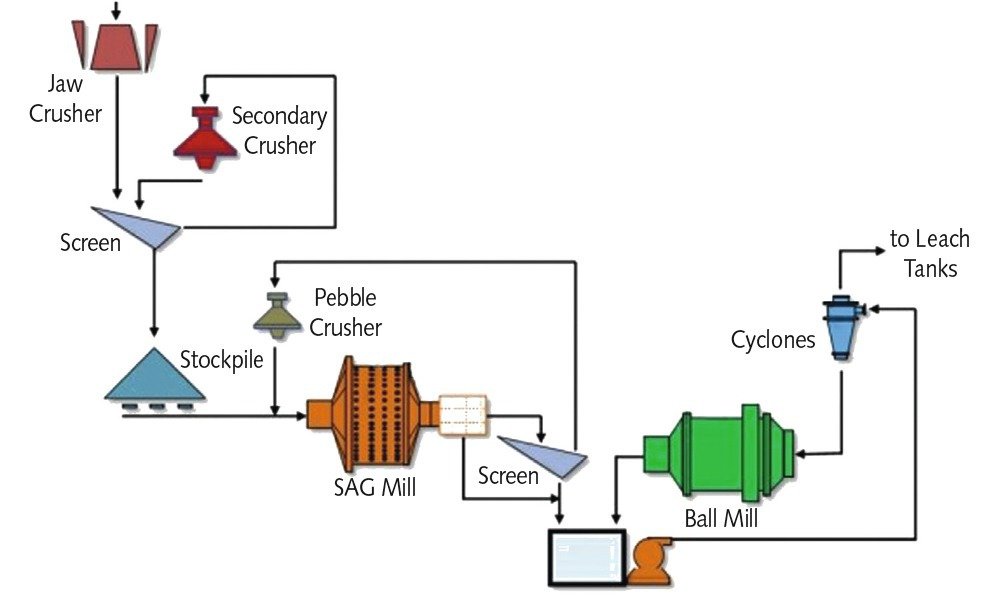
Crushing typically follows this sequence:
- Primary Crushing: Large rocks from the mine are reduced using jaw or gyratory crushers.
- Secondary Crushing: Further size reduction using cone or impact crushers.
- Tertiary/Quaternary Crushing (if needed): For fine grinding, especially in gold and lithium processing.
- Screening: Separates crushed material by size for efficient downstream processing.
Modern mines use mobile and semi-mobile crushing plants, while artisanal sites may rely on manual or small-scale mechanical crushers.
4. Key Countries with Active Mining and Crushing Operations
- South Africa: Major hub for gold, platinum, and coal with advanced crushing facilities
- Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): Copper and cobalt mines use large-scale crushing and processing
- Ghana and Mali: Gold mines feature modern crushing and milling circuits
- Zambia: Copper belt mines operate integrated crushing and flotation plants
- Zimbabwe: Lithium and gold projects include dedicated crushing and spodumene concentration
- Namibia and Botswana: Diamond and base metal operations with controlled crushing to preserve gem quality
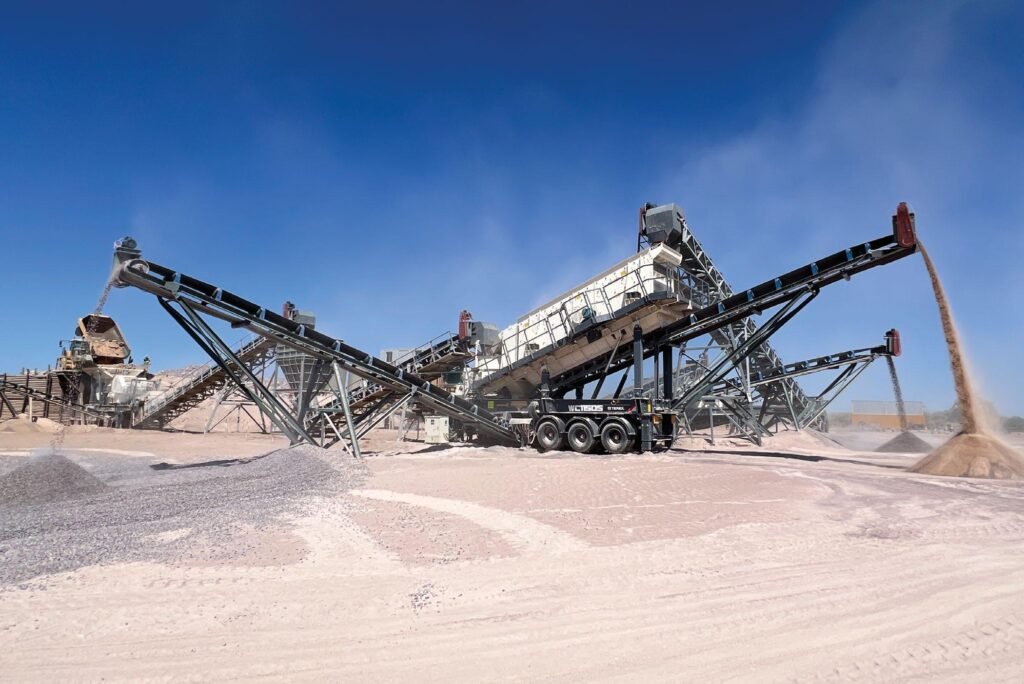

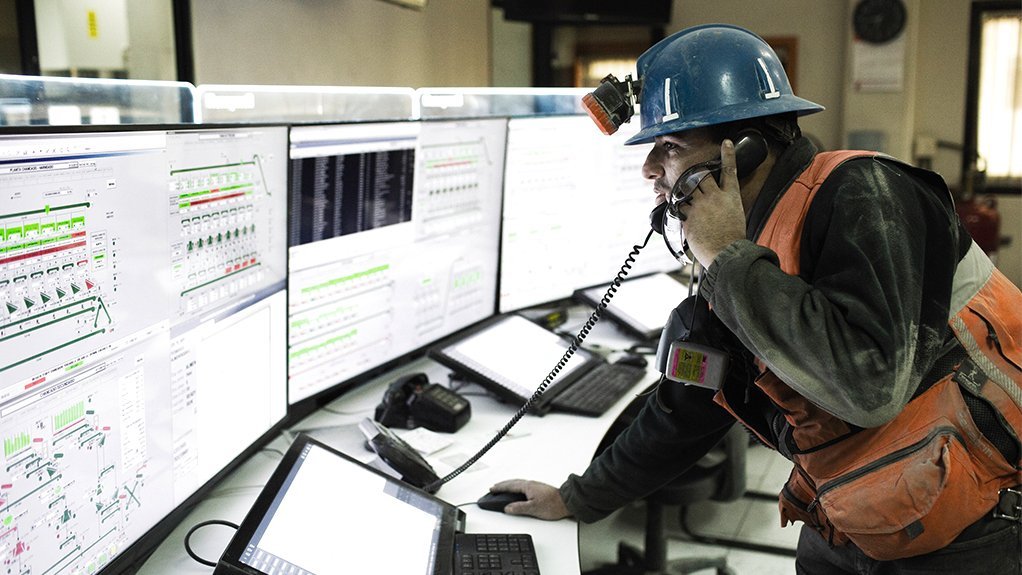
5. Technology and Trends in Crushing
- Automation and digital monitoring improve efficiency and reduce downtime
- Modular crushing plants are used in remote areas for faster deployment
- Energy-efficient crushers help reduce carbon footprint
- Artisanal miners are increasingly adopting small diesel-powered crushers to improve productivity
There is also growing investment in local beneficiation—processing raw ore within Africa—to add value before export.

FAQs
Q1: What is crushing in mining?
A1: Crushing is the process of breaking large rocks into smaller pieces so valuable minerals can be extracted efficiently.
Q2: Why is crushing important in African mining?
A2: It prepares ore for further processing like leaching, flotation, or gravity separation, improving recovery rates.
Q3: Do artisanal miners use crushers?
A3: Yes, many now use small mechanical crushers to increase output, though safety and environmental concerns remain.
Conclusion
Mining and crushing in Africa form the backbone of the continent’s mineral industry. From gold in Ghana to lithium in Zimbabwe, effective crushing operations are essential for transforming raw ore into valuable commodities for global markets. As technology advances, Africa is poised to strengthen its role in the global mineral supply chain.

