South Africa Mining Registry
South Africa Mining Registry: A Comprehensive Guide to Mineral Rights and Ownership
The South Africa Mining Registry is a critical component of the country’s mining governance framework, providing transparency and accountability in the management of mineral resources. As one of the world’s largest producers of gold, platinum group metals (PGMs), diamonds, and coal, South Africa relies on its mining registry to track mineral rights, ownership, and compliance with regulatory requirements. In this blog post, we will explore the purpose of the mining registry, its key features, how it supports transparency and investment, and the challenges it faces.

What is the South Africa Mining Registry?
The South Africa Mining Registry is a centralized system managed by the Department of Mineral Resources and Energy (DMRE) that tracks all mineral rights, exploration permits, mining licenses, and related documentation. It serves as a public record of who owns what in the mining sector, ensuring transparency and accountability in the allocation and use of mineral resources.
The registry operates under the Mineral and Petroleum Resources Development Act (MPRDA) of 2002, which mandates that all mineral resources belong to the state and must be allocated through a transparent and competitive process.
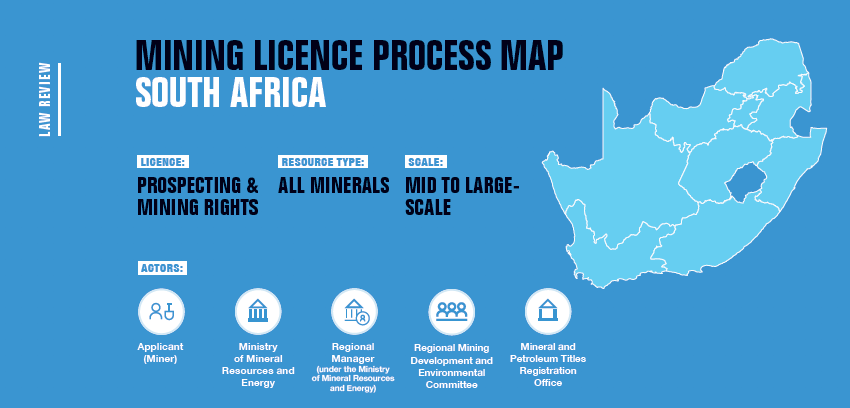
Key Features of the Mining Registry
1. Tracking Mineral Rights
The registry maintains comprehensive records of all mineral rights, including:
- Exploration Rights : Permits for prospecting and exploration activities.
- Mining Rights : Licenses for extracting and processing minerals.
- Retention Permits : Permissions to retain mining rights while awaiting favorable market conditions.
2. Ownership Information
The registry provides details about the entities or individuals holding mineral rights, including companies, consortia, and foreign investors. This ensures clarity on ownership structures and prevents disputes.
3. Compliance Monitoring
Mining companies are required to submit regular reports on their operations, environmental impact, and community engagement efforts. The registry tracks compliance with these obligations, enabling regulators to enforce penalties for non-compliance.

4. Public Access
While certain sensitive data is restricted, much of the registry’s information is accessible to the public. This promotes transparency and allows stakeholders—such as investors, communities, and NGOs—to monitor mining activities.
Importance of the Mining Registry
1. Promoting Transparency
By maintaining a public record of mineral rights and ownership, the registry reduces corruption and ensures equitable allocation of resources. This builds trust among stakeholders and fosters a fair operating environment.
2. Supporting Investment
Investors rely on the registry to verify the legitimacy of mining rights and assess risks before committing capital. A well-maintained registry attracts foreign direct investment (FDI) by providing clarity and reducing uncertainty.
3. Ensuring Accountability
The registry holds mining companies accountable for their operations, particularly in areas like environmental protection and community benefit-sharing. This alignment with global best practices enhances the industry’s reputation.
4. Facilitating Dispute Resolution
Clear records of mineral rights and ownership help resolve conflicts between companies, communities, and government authorities. This reduces legal disputes and promotes stability in the sector.
Challenges Facing the Mining Registry
1. Outdated Systems
Portions of the registry still rely on manual processes and outdated technology, leading to inefficiencies and delays in processing applications or updates.
2. Data Accuracy
Inaccurate or incomplete data can undermine the registry’s effectiveness. For example, discrepancies in ownership records may lead to disputes or illegal mining activities.
3. Limited Public Awareness
Many stakeholders, particularly local communities, are unaware of how to access or interpret registry data. Increasing awareness and accessibility is essential for maximizing its impact.
4. Regulatory Overlaps
Conflicts between national, provincial, and local regulations can create confusion about which authority oversees specific aspects of the registry, delaying decision-making.
Recent Developments and Digitalization Efforts
1. Online Portal Implementation
The DMRE has launched an online portal for the mining registry, allowing stakeholders to apply for rights, track applications, and access records digitally. This initiative aims to streamline processes and improve transparency.
2. Integration with Environmental Systems
The registry is being integrated with environmental management systems to ensure that companies comply with sustainability requirements before obtaining mining rights.
3. Blockchain Technology Exploration
South Africa is exploring the use of blockchain technology to enhance the security and immutability of registry data. This could prevent fraud and ensure accurate tracking of mineral rights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the purpose of the South Africa Mining Registry?
A1: The registry tracks mineral rights, ownership, and compliance, ensuring transparency and accountability in the mining sector.
Q2: Who manages the South Africa Mining Registry?
A2: The registry is managed by the Department of Mineral Resources and Energy (DMRE).
Q3: Can the public access the mining registry?
A3: Yes, much of the registry’s information is publicly accessible, though some sensitive data may be restricted.
Q4: How does the registry support investment in mining?
A4: By providing clear records of mineral rights and ownership, the registry reduces uncertainty and builds investor confidence.

