Africa Mining Legislation Atlas
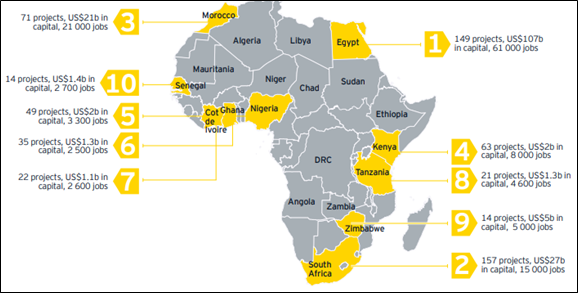
Africa is home to some of the world’s most valuable mineral resources, and as the continent’s mining sector continues to grow, understanding the legal frameworks and legislation governing mining activities has become increasingly important. From licensing procedures to environmental regulations , community engagement requirements , and taxation policies , each country in Africa has its own set of rules that shape how mining operations are conducted.
This Africa Mining Legislation Atlas provides an overview of the key legal aspects in several major African mining nations, helping investors, professionals, and stakeholders navigate the complex regulatory environment.
Key Elements of Mining Legislation in Africa
- Licensing and Exploration Rights
- Most African countries require companies to obtain exploration and mining licenses from national or regional authorities.
- These licenses often include conditions related to environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and community consultations.
- Environmental Regulations
- Many African governments have introduced stricter environmental laws to ensure responsible mining practices.
- Companies are typically required to submit Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) before starting operations.
- Community Engagement and Local Content Laws
- Several countries, such as South Africa , Ghana , and Zambia , have implemented policies requiring mining companies to engage with local communities and prioritize local employment and procurement.
- Taxation and Royalties
- Mining companies are subject to various taxes, including royalty payments , corporate income tax , and resource-based levies .
- Some countries offer tax incentives to attract foreign investment.
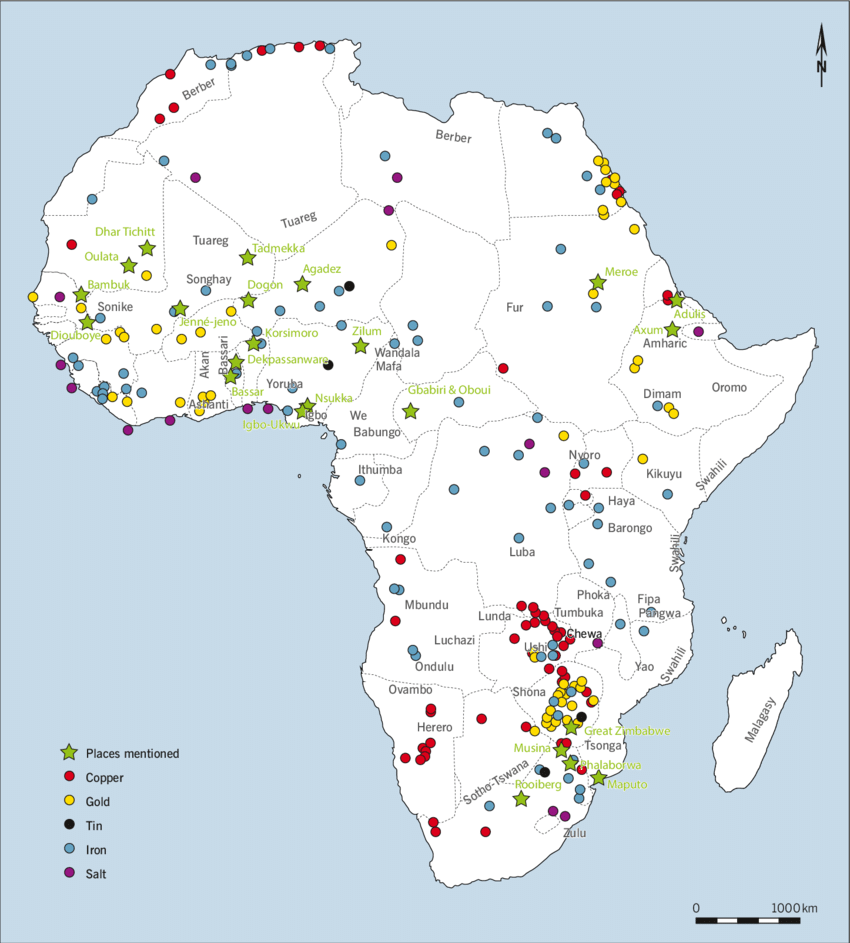
Country-Specific Overview
South Africa
- Legislation : Mineral and Petroleum Resources Development Act (MPRDA)
- Key Features : Emphasis on local content , community benefits , and environmental compliance .
- Licensing : Requires mining rights and exploration permits through the Department of Mineral Resources and Energy.

Ghana
- Legislation : Mining Law 2016 (Act 939)
- Key Features : Focus on transparency , anti-corruption measures , and benefits sharing with local communities.
- Licensing : Requires mining licenses and environmental approvals from the Geological Survey of Ghana .
Kenya
- Legislation : Mining Act 2016
- Key Features : Encourages foreign investment , promotes local participation , and mandates environmental protection .
- Licensing : Managed by the Kenya Mining Board and requires environmental impact assessments .
Zambia
- Legislation : Mining and Minerals Act 2015
- Key Features : Emphasis on national ownership , revenue sharing , and responsible mining .
- Licensing : Governed by the Zambia Mining Council and requires environmental clearances .
Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
- Legislation : Mining Code 2018
- Key Features : Aims to improve governance , reduce corruption, and promote local development .
- Licensing : Managed by the National Agency for the Promotion of Mining (ANPM) and includes community consultation requirements.
Why Understanding Mining Legislation Matters
For investors, operators, and local communities, a clear understanding of mining legislation is essential for:
- Ensuring compliance with national and international standards
- Avoiding legal risks and fines
- Building trust with local communities
- Securing long-term viability of mining projects
FAQs
Q: What is the Africa Mining Legislation Atlas?
A: It is a guide that outlines the legal frameworks and mining policies across African countries, helping stakeholders understand the regulatory environment.
Q: Are there differences in mining laws across African countries?
A: Yes, each country has its own set of mining laws, focusing on different aspects such as licensing, environmental protection, and community engagement.
Q: How can I access mining legislation in Africa?
A: You can find mining laws on government websites, through legal databases, or via platforms like African Mining IQ .

