What Is Mining in Africa?

Mining in Africa refers to the extraction of valuable minerals and natural resources from the Earth, playing a critical role in many African economies. The continent is rich in gold, diamonds, copper, cobalt, lithium, platinum, and other critical minerals, making it a key supplier to the global market.
Here’s a concise overview of mining in Africa, its importance, key minerals, and challenges.
1. Overview of Mining in Africa
Africa is home to some of the world’s largest and richest mineral deposits. Mining is a major economic sector in many African countries, contributing to GDP, employment, and export earnings.
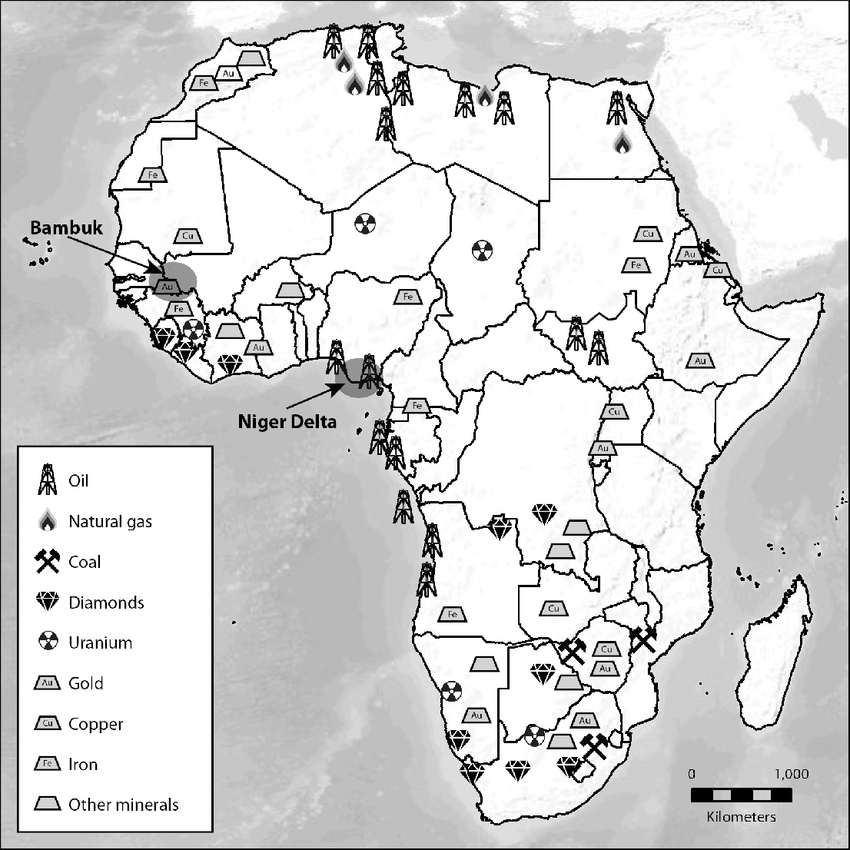
2. Major Minerals Mined in Africa
Africa produces a wide range of minerals, including:
- Gold: Ghana, South Africa, Mali, Tanzania
- Diamonds: Botswana, DRC, Angola
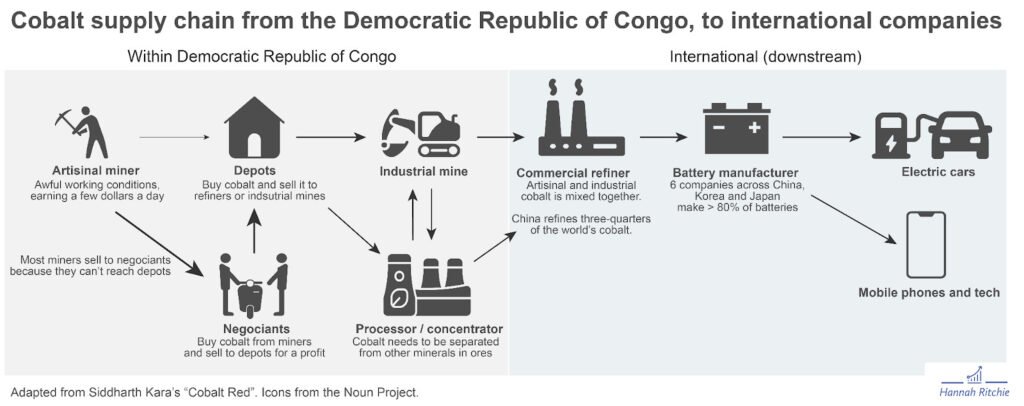
- Cobalt: Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) – supplies over 70% of global cobalt
- Copper: Zambia, DRC
- Lithium: Zimbabwe, Namibia, Mali
- Platinum Group Metals (PGMs): South Africa – world’s largest producer
- Bauxite: Guinea – holds the largest bauxite reserves
- Iron Ore: Liberia, Algeria
These minerals are essential for technology, energy, and industrial applications.
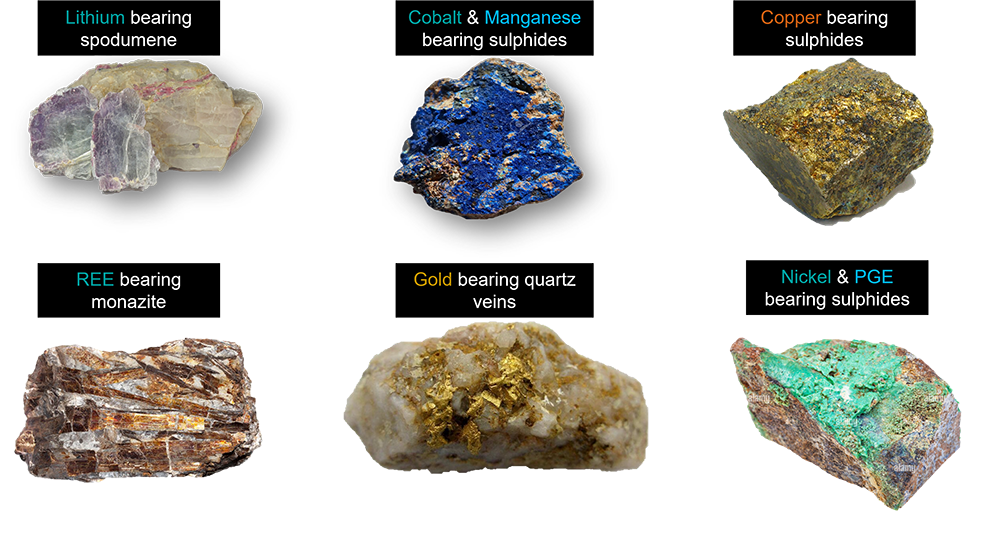

3. Key Mining Countries in Africa
Several African countries are known for their mineral wealth:
- South Africa: Gold, platinum, chromium
- DRC: Cobalt, copper, coltan
- Zambia: Copper belt, cobalt
- Guinea: Bauxite, iron ore
- Ghana: Gold, manganese
- Mali: Gold
- Zimbabwe: Platinum, lithium
- Angola: Diamonds, oil
- Tanzania: Gold, tanzanite
These countries rely heavily on mining for economic growth and development.

4. Types of Mining in Africa
There are three main types of mining in Africa:
- Industrial-scale mining: Operated by multinational companies using advanced technology
- Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM): Manual mining by local communities
- Offshore mining: Oil and gas extraction in countries like Nigeria and Angola
Each type has different economic, social, and environmental impacts.

5. Mining and the Global Supply Chain
Africa plays a strategic role in the global supply chain, especially for:
- Cobalt – essential for EV batteries
- Lithium – key for renewable energy and battery production
- Copper – used in electric vehicles and power grids
- Coltan – used in smartphones and electronics
As the world shifts toward clean energy and digital technology, Africa’s mining sector is becoming increasingly important.
FAQs
Q1: Why is mining important in Africa?
A1: Mining is a major source of government revenue, jobs, and foreign investment for many African countries.
Q2: Which African country is the largest miner?
A2: The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is one of the most significant due to its cobalt and copper production.
Q3: Is lithium mined in Africa?
A3: Yes, particularly in Zimbabwe, Namibia, and Mali, where lithium pegmatite deposits are being developed.
Conclusion
Mining in Africa is a major economic driver, rich in gold, cobalt, lithium, and diamonds. While the sector faces governance and sustainability challenges, it also offers huge potential for growth, industrialization, and global supply chain integration, especially in the clean energy and technology sectors.

